Introduction to the architecture¶
GameBus FHIR layer is built on a tech stack of open-source softwares (see diagram below), comprising two major components:
Mapping engine
Mapping engine is a component to convert data from one format to another, e.g. from GameBus JSON data to FHIR JSON data.
Google HCLS Data Harmonization is used as the mapping engine of GameBus FHIR layer. The engine supports transformation between any two formats or schemas by configuring mapping rules. The mapping rules can be configured using protobuf format or Whistle Data Transformation Language that will be automatically transpiled to protobuf. Because of that, we use Google Whistle or GW to refer to this mapping engine.
FHIR web server
FHIR web server is the server to provide the capabilities FHIR REST API.
HAPI FHIR framework is used to add these capabilities to GameBus FHIR layer. With this framework, a HAPI FHIR plain server was created and some resource providers were defined to serve up FHIR resources, e.g. Patient and Observation.
The FHIR server has two functionalities in GameBus FHIR layer:
It forwards the user’s HTTP request to GameBus REST API after transforming the request for FHIR REST API to the request for GameBus API.
It gets FHIR-compliant data from mapping engine and sends these data to the user as HTTP response through FHIR REST API.
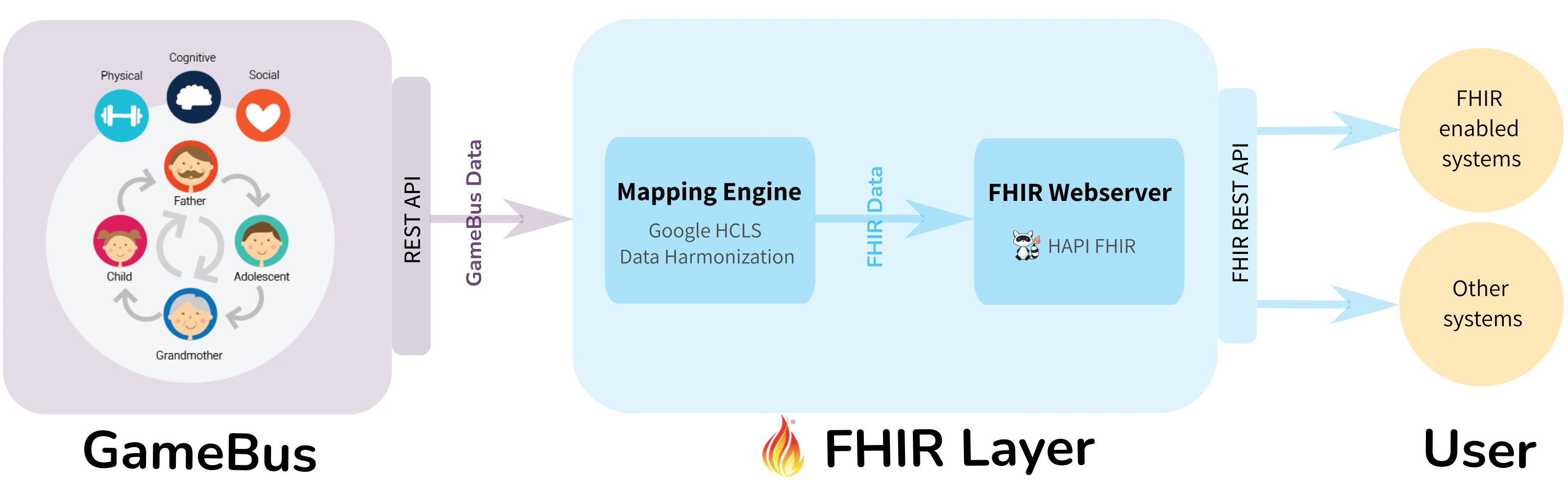
One of the advantages of this tech stack is that it does not change any code or schema of GameBus platform, but just add one more layer on the existing platform to add the capabilities of FHIR REST API. Moreover, though this FHIR layer is developed for GameBus platform, the tech stack can be easily applied to other healthcare platforms to enable FHIR service.